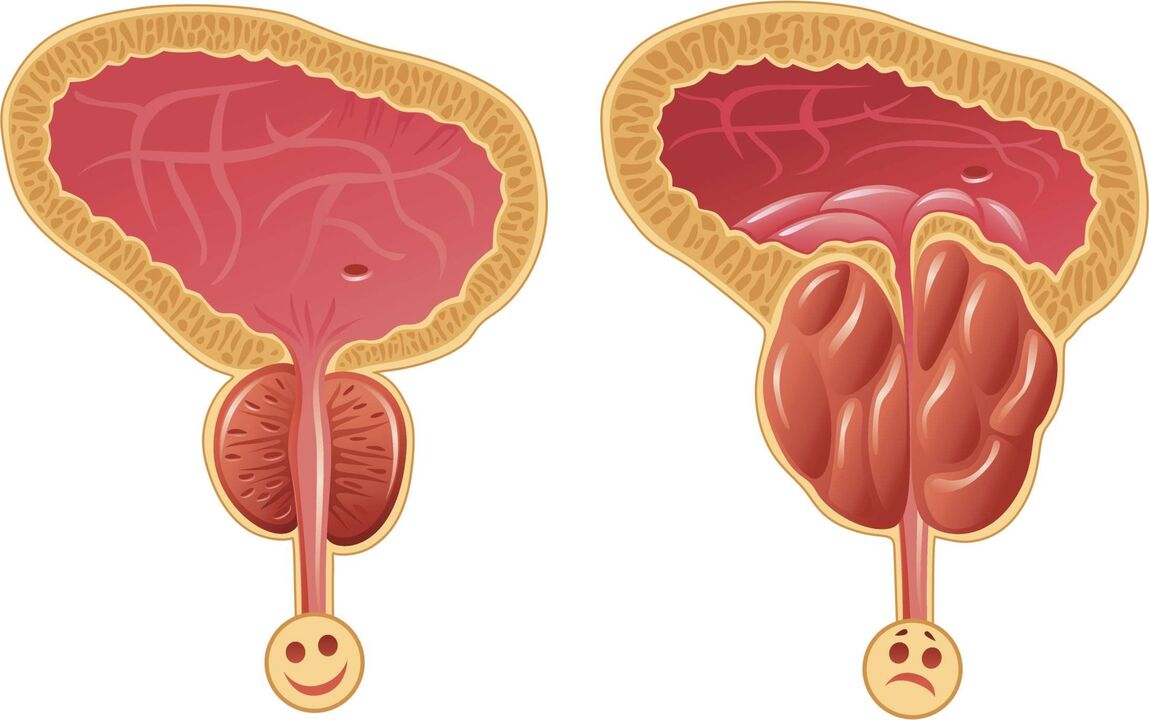
What is prostatitis?
- bacteria;
- Nonbacterial prostatitis.
Bacteria aren't always the cause of prostate inflammation
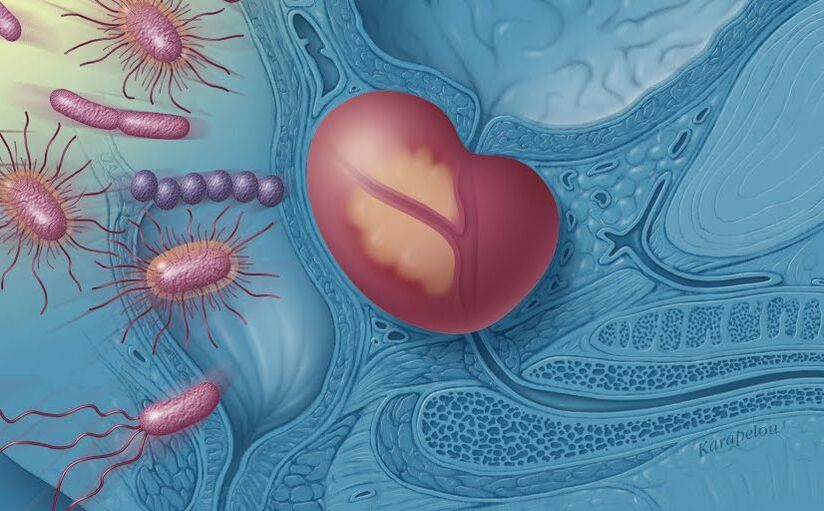
Causes of prostatitis
- recurring urinary tract infections;
- bladder catheterization;
- Surgery in the genitourinary area;
- Unprotected anal sex.
bacterial prostate
nonbacterial prostatitis
- Impaired immune response;
- Central nervous system disease, which affects the nerves and muscles of the genitourinary system and prevents a person from emptying the bladder normally;
- Mental disorders such as stress, anxiety, or depression.
Typical symptoms of prostatitis
- Frequent urination;
- burning sensation when urinating (usually small amounts of urine);
- Bladder and perineal pain;
- Pain during bowel movements;
- feel sick and vomit;
- Fever and chills.

Special situation: asymptomatic prostatic inflammation
diagnosis
Treatment of prostatitis
Treatment of bacterial prostatitis
- If it is mild acute prostatitis, the doctor must prescribe fluoroquinolone antibiotics, which the patient must take for 10 days.
- If the inflammation is severe, your doctor may give you a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
- If the inflammation is chronic, patients usually take fluoroquinolones for 4-6 weeks.
Treatment of nonbacterial prostatitis
Treat prostatitis with folk remedies
weeds

- Pour 1 heaped teaspoon of the herb into 1/4 liter of water, bring to a boil and brew briefly (15 minutes). You should drink it in small sips (up to 2 cups) throughout the day.
- Suitable for all prostate diseases, including prostate cancer;
- for kidney disease;
- For bladder disorders;
- for bladder cancer;
- Used for wound healing.
green tea
nettle
cranberry

ginger
pumpkin seeds